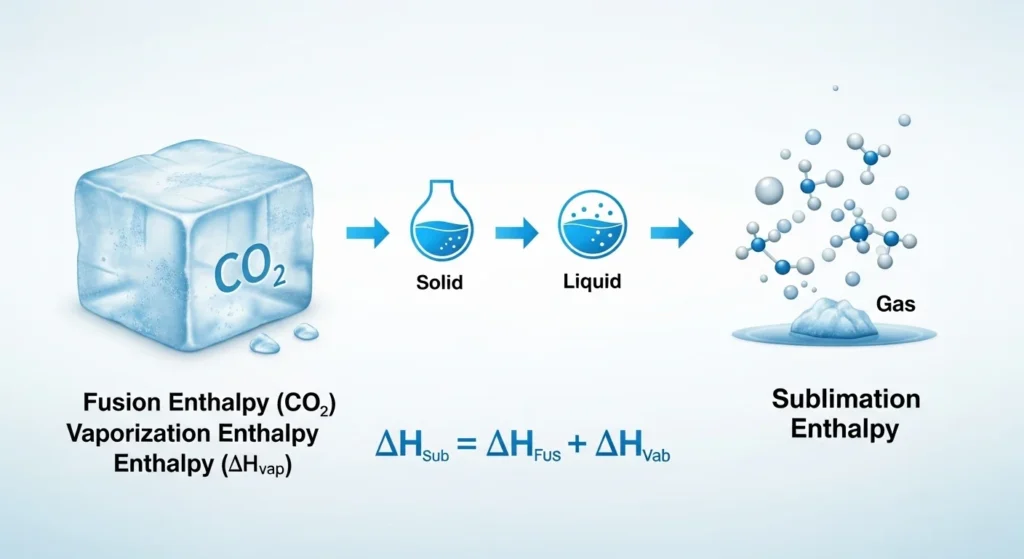
The sublimation enthalpy calculator helps you find the energy needed to convert a solid directly into a gas. It uses the simple formula ΔH_sub = ΔH_fus + ΔH_vap, where ΔH_fus is the enthalpy of fusion and ΔH_vap is the enthalpy of vaporization.
By entering these two values, the calculator instantly provides the enthalpy of sublimation in kJ/mol.
For example, if a substance has ΔH_fus = 5.0 kJ/mol and ΔH_vap = 40.0 kJ/mol, the sublimation enthalpy will be 45.0 kJ/mol. This tool is widely used in chemistry and thermodynamics to study phase changes such as dry ice turning into gas.
Sublimation Enthalpy Calculator
Formula Used in the Calculator
Formula:
ΔHsub = Enthalpy of sublimation (in kJ/mol)
ΔHfus = Enthalpy of fusion (in kJ/mol)
ΔHvap = Enthalpy of vaporization (in kJ/mol)

Where:
- ΔH_sub = Enthalpy of sublimation (in kJ/mol)
- ΔH_fus = Enthalpy of fusion (in kJ/mol) (energy required to melt a solid into a liquid)
- ΔH_vap = Enthalpy of vaporization (in kJ/mol) (energy required to convert a liquid into a gas)
How to Use the Calculator
- Enter the Fusion Enthalpy (ΔH_fus) in the provided input box.
- Enter the Vaporization Enthalpy (ΔH_vap) in the second input box.
- Click the "Calculate Sublimation Enthalpy" button to compute the result.
- The calculator will display the sublimation enthalpy value in kJ/mol.
This tool is useful in thermodynamics and chemistry for understanding phase changes, particularly for sublimation processes like dry ice (solid CO₂) turning into gas directly.
Example Calculation for Sublimation Enthalpy
Let's assume we have a substance with the following enthalpies:
- Temperature: 300 K (if required)
- Fusion Enthalpy (ΔH_fus) = 5.0 kJ/mol
- Vaporization Enthalpy (ΔH_vap) = 40.0 kJ/mol

Why is Sublimation Enthalpy Important?
- Industrial Uses: Freeze-drying food/pharmaceuticals.
- Planetary Science: Explains comet tails (sublimating ices).
- Material Engineering: Critical for vapor deposition techniques.
Final Answer:
The sublimation enthalpy for this substance is 45.0 kJ/mol.
This means that 45.0 kJ of energy is required per mole to convert the substance directly from a solid to a gas.
References
- NIST Chemistry WebBook – Authoritative thermodynamic data.
- Atkins, P., & de Paula, J. (2018). Physical Chemistry (11th ed.). Oxford University Press. Theoretical foundation.