Opposite of Sublimation: How Deposition Works in Science
It’s called deposition, when a gas turns directly into a solid, skipping the liquid phase. Think of frost forming on a cold window: water vapor in the air becomes ice crystals without ever becoming liquid.
While sublimation needs heat (like dry ice vanishing), deposition requires cooling. Both are rare in everyday life but crucial in science, from weather patterns to industrial coatings.
While sublimation is when a solid turns directly into a gas (like dry ice disappearing into vapor), deposition is the reverse, where a gas transforms straight into a solid (like frost forming on a cold window).
These two processes are fascinating because they skip the liquid phase entirely. But how exactly do they work, and where do we see them in real life?
Sublimation vs. Deposition: The Phase Change Twins
Sublimation and deposition are two sides of the same scientific coin – one disappears, the other appears, both magically skipping the liquid stage!
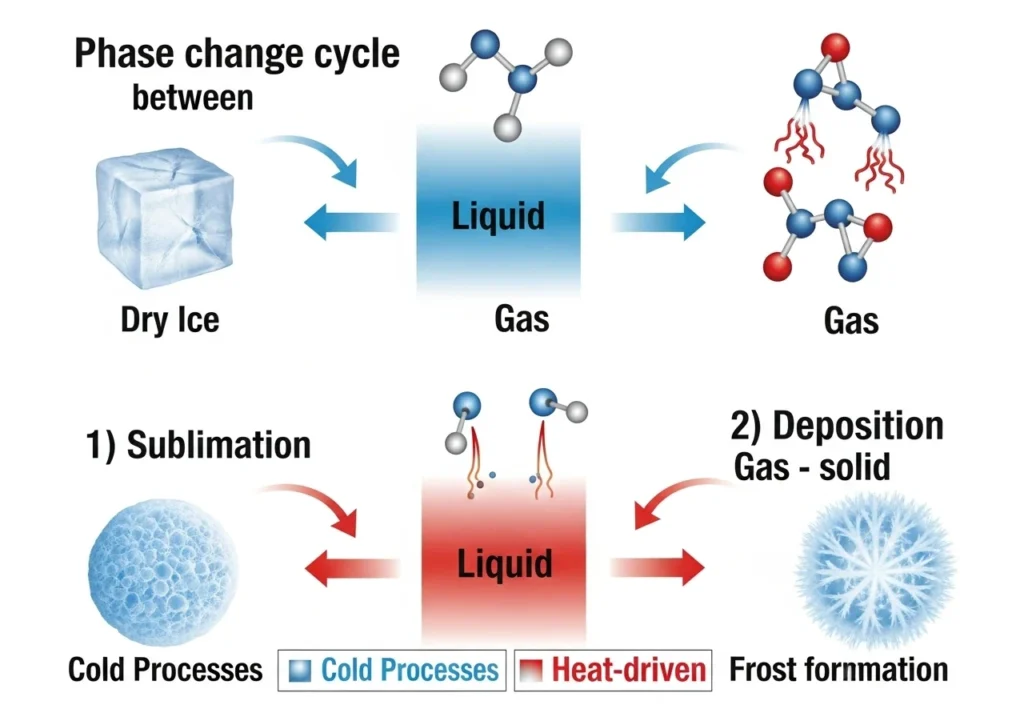
Sublimation: When Solids Vanish into Thin Air
- What happens: Solid → Gas (no liquid in between)
- Why it happens: Molecules gain enough energy to break free
- Real-world example: Dry ice “smoke” at parties (-78.5°C transformation)
- Cool fact: This is how freezer burn dehydrates food!
Deposition: When Gas Materializes as Solid
- What happens: Gas → Solid (straight to frosty form)
- Why it happens: Molecules lose energy and lock into place
- Real-world example: Winter frost patterns on your windshield
- Cool fact: This creates snowflakes in clouds!
You’ve seen both in action – now you know the science behind these everyday wonders!

Now that we clearly understand sublimation let’s explore its antithesis.
The Science Behind Phase Changes
Phase changes occur when matter shifts between solid, liquid, and gas states. Sublimation and deposition are unique because they skip the liquid phase entirely
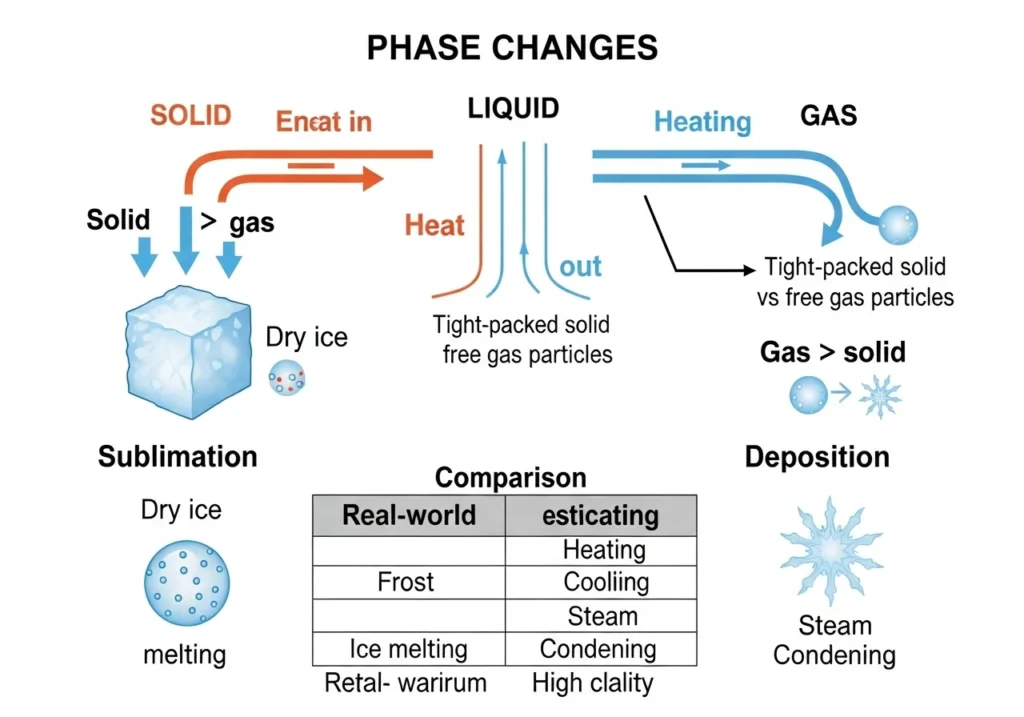
How They Work
✔ Sublimation (Solid → Gas)
- Requires energy input to break molecular bonds
- Example: Dry ice (-78.5°C) turning into CO₂ gas
✔ Deposition (Gas → Solid)
- Occurs when gas loses energy rapidly
- Example: Frost forming on a cold window
Comparison to Other Phase Changes
| Process | Change | Energy | Example |
|---|---|---|---|
| Melting | Solid → Liquid | Added | Ice → Water |
| Freezing | Liquid → Solid | Removed | Water → Ice |
| Evaporation | Liquid → Gas | Added | Boiling water → Steam |
| Condensation | Gas → Liquid | Removed | Dew forming on grass |
Key Factor: Molecular energy determines whether substances transform—adding heat excites molecules, while cooling slows them down.
Understanding Phase Changes
|
Phase Change |
Energy Change |
Temperature and Pressure Conditions |
Example |
|---|---|---|---|
|
Sublimation |
Solid gains energy |
Occurs at specific low temperatures and low pressures |
Dry ice (solid CO₂) sublimes at -78.5°C |
|
Deposition |
Gas loses energy |
Occurs when gas comes into contact with a cold surface |
Frost forming on a window |
|
Melting |
Solid gains energy |
Occurs at the melting point of the substance |
Ice melting into water |
|
Freezing |
Liquid loses energy |
Occurs at the freezing point of the substance |
Water freezing into ice |
|
Evaporation |
Liquid gains energy |
Occurs at the boiling point or below if energy is sufficient |
Water evaporating into steam |
|
Condensation |
Gas loses energy |
Occurs when gas is cooled below its condensation point |
Steam condensing into water |
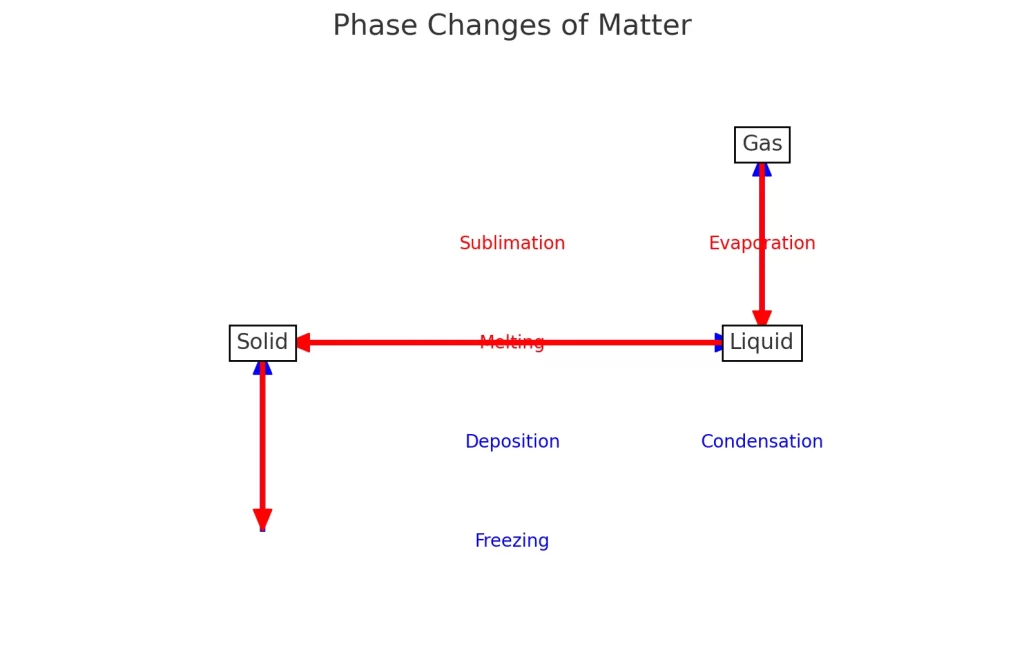
Chart showing the phase changes of matter. It illustrates how substances transition between solid, liquid, and gas states through processes like sublimation, deposition, melting, freezing, evaporation, and condensation.
- Sublimation: Solid to Gas
- Deposition: Gas to Solid
- Melting: Solid to Liquid
- Freezing: Liquid to Solid
- Evaporation: Liquid to Gas
- Condensation: Gas to Liquid
The Fascinating Science of Deposition
Deposition: Nature’s Reverse Magic
While sublimation makes solids vanish into gas, deposition performs the opposite miracle – transforming invisible gas directly into solid matter. This occurs when gas particles lose energy and bond together on surfaces, skipping the liquid phase entirely.
Why Deposition Matters in Science
- The exact inverse process of sublimation
- Requires precise temperature/pressure conditions
- Creates ordered solid structures from chaotic gas particles
- Fundamental to both natural phenomena and industrial applications
Real-World Applications of Deposition
1️⃣ Thin Film Technology
How it works:
- Atomic-level material layering onto surfaces
- Enables nanotechnology manufacturing
Key Uses:
✔ Semiconductor chips
✔ Solar panel coatings
✔ Anti-reflective lenses
2️⃣ Protective Armor for Machines
Industrial Benefits:
- Corrosion-resistant aerospace coatings
- Ultra-hard surfaces for cutting tools
- Thermal barriers in jet engines
3️⃣ Medical Marvels
Pharmaceutical Advances:
- Improved drug absorption
- Time-release drug capsules
- Precision medication dosing
The Role of Deposition in Nanotechnology
Nanotechnology, a field at the cutting edge of scientific exploration, heavily relies on deposition processes. Researchers use these techniques to fabricate nanoscale structures and devices with remarkable precision. From nanowires to quantum dots, deposition opens the door to many possibilities in the nanoworld.
🌌 Beyond Basic Phase Changes
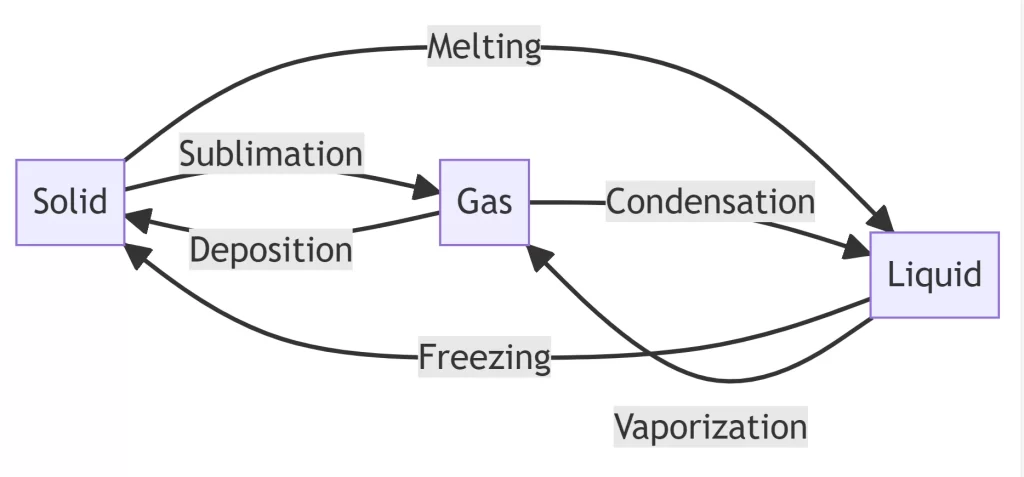
🔁 The Complete Phase Change Family
While sublimation and deposition are fascinating, they’re part of a larger family of matter transformations:
- 🧊→💧 Melting (solid to liquid)
- 💧→🧊 Freezing (liquid to solid)
- 💧→☁️ Vaporization (liquid to gas)
- ☁️→💧 Condensation (gas to liquid)
- 🧊→☁️ Sublimation (solid to gas)
- ☁️→🧊 Deposition (gas to solid)
🔥 Sublimation
🧪 Definition: Solid → Gas (skips liquid)
❄️ Example: Dry ice disappearing at -78.5°C
🏭 Uses: Freeze-drying, printing, preservation
🧊 Fusion (Melting)
🧪 Definition: Solid → Liquid
🔥 Example: Ice melting at 0°C
🏭 Uses: Cooking, metalworking, manufacturing
🌐 Real-World Applications

Sublimation vs. Fusion: Key Differences
| Aspect | Sublimation | Fusion |
|---|---|---|
| Phase Change Path | Solid → Gas (skips liquid) | Solid → Liquid |
| Energy Requirements | High energy to break solid bonds directly | Moderate energy to melt solid |
| Conditions | Low Pressure, below triple point | At melting point for given pressure |
| Practical Uses | Preservation, Printing | Manufacturing, Cooking |
Ready to Bring Science to Life?
At Subli Genius Print, we master the art and science of sublimation, helping you harness these processes in practical, innovative ways.
As we examine the duality of sublimation and deposition, we gain profound insights into the fascinating processes that shape materials science.
Share Your Experiences
Have you noticed frost forming on windows or experienced freezer burn? What intrigued you most about these phenomena? We’d love to hear your stories!




One Comment